Cashless
Defining OPD cashless claims, advantages, challenges, & typical workflow
Cashless health insurance allows policyholders/beneficiaries to receive medical treatment without having to pay upfront to the providers for the medical services/treatment. It covers both outpatient department (OPD) and inpatient department (IPD) expenses, providing financial relief to the beneficiaries.
Advantages of cashless claims
Improves patient experience : Cashless insurance enhances the overall beneficiary experience by streamlining the healthcare process. It reduces the administrative hassles of reimbursement claims and paperwork submission.
Financial relief : By covering medical expenses directly, cashless insurance reduces the financial burden on policyholders/beneficiaries during times of illness or emergencies.
Access to quality care : Cashless insurance often partners with a network of hospitals and healthcare providers, ensuring access to quality medical facilities and specialists for policyholders.
Prompt treatment : Beneficiaries can plan prompt medical treatment, without having to worry about arranging funds before getting the necessary care.
Challenges
Limited network : Cashless insurance poses a challenge when policyholders require immediate care from healthcare providers outside the insurer's network, leading to out-of-pocket expenses.
Pre-authorization/claims delays : Delays in obtaining pre-authorization/claims for OPD can hinder prompt treatment and causes inconvienience for both providers and beneficiaries.
Frauds : As the OPD claims adjudication is time sensitive; possibility of the impersonation/identity theft, phantom service, etc. frauds increases further.
Typical/existing workflow for OPD cashless claims
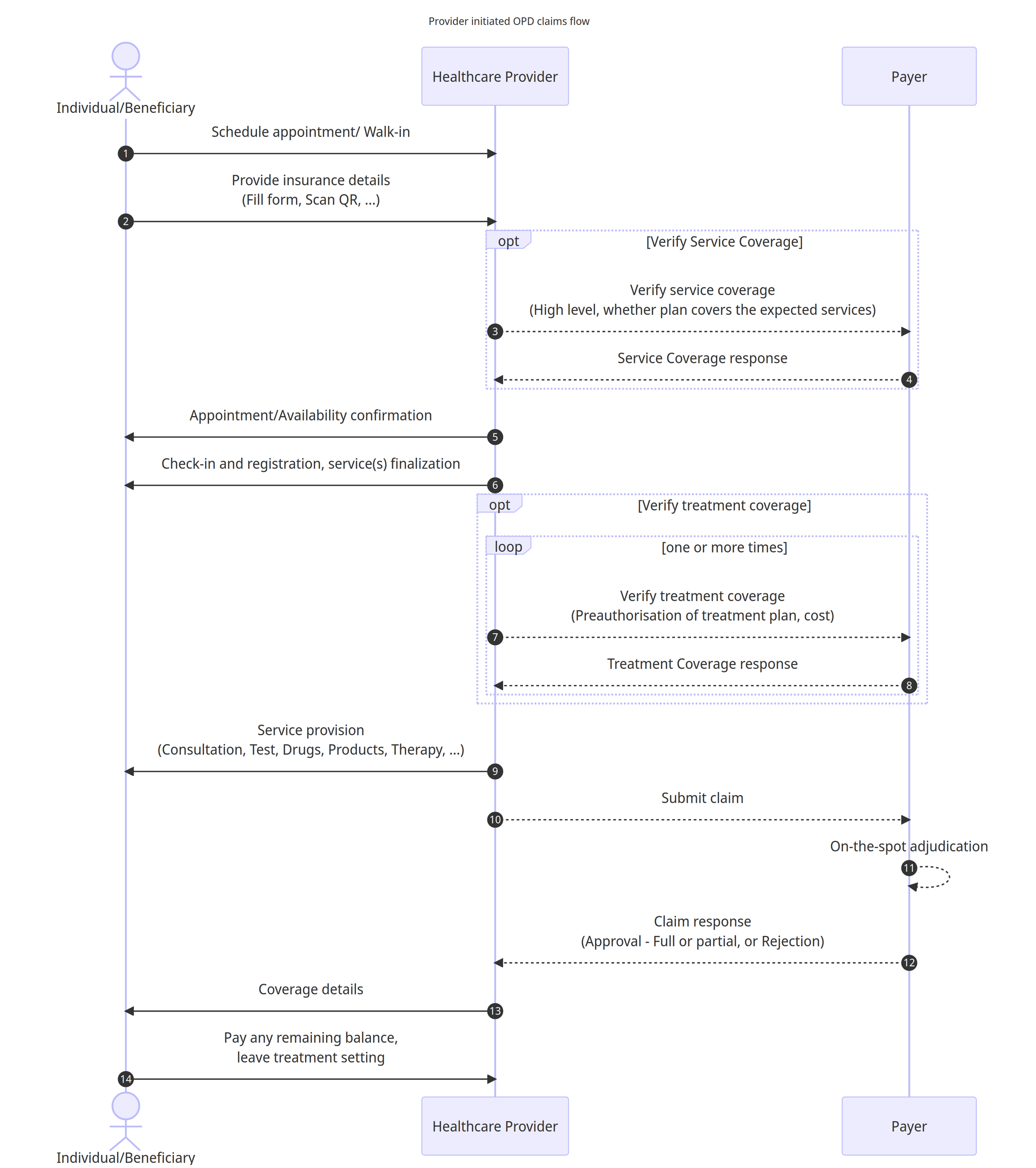
Workflow details
An individual/Beneficiary schedules an appointment or arrives as a walk-in (emergency) at the healthcare provider's facility
The individual/Beneficiary provides necessary details including insurance details, which may involve filling out a form or scanning a QR code to share relevant information.
(Optional) The Healthcare Provider initiates a coverage verification process by contacting the Payer to confirm the high-level service coverage, aiming to determine if the expected services are covered under the Individual's insurance plan.
(Optional) The payer responds back with coverage eligibility details of the plan.
The Healthcare Provider confirms the admission for the individual/beneficiary.
The individual/beneficiary proceeds with the check-in, registration, and finalisation of required service(s) based on their needs and preferences.
(Optional) The Healthcare Provider further engages with the payer to verify treatment coverage, seeking preauthorization for the proposed treatment/service plan and involved cost details as required by the insurance policy. Wherever applicable, this step may be repeated multiple times to signal change in treatment/service plan.
The payer responds back with the preauthorization response for each request alongwith the pre-authorized amount for each procedure, product, service, etc.
The healthcare provider provides the necessary services to the Individual, which may include a range of medical procedures, tests, administration of drugs, products, therapy sessions, or any other relevant treatments.
The healthcare provider initiates the claim submission process by forwarding the relevant details and documents to the payer.
The payer performs the on-the-spot adjudication to evaluate the submitted claim
The payer responds to the healthcare provider with either approval (full or partial) or rejection of the claim.
After receiving the claim response from the payer, the healthcare provider communicates the claim details to the individual, informing them about the approved services and any payment obligations that remain.
The individual proceeds with any necessary payments, settling any remaining balance based on the coverage provided by the insurance policy, and subsequently concludes the treatment or service provision setting.
Following subsection details out the typical workflow for the reimbursement claims for OPD.
Last updated
Was this helpful?