Reimbursement
Defining OPD reimbursement claims, advantages, challenges, & typical workflow
In the Reimbursement scenario, the onus is on the patient to duly submit all the necessary documents and share the information with the insurer as required for processing the claim.
Here, we will explore the advantages and challenges associated with reimbursement claims in healthcare.
Advantages of Reimbursement Claims in Healthcare
Wider access for policyholders: Enables access to out-of-network healthcare services and providers, and when cashless authorisation is denied by the insurer. Reimbursement claims help make healthcare services more accessible to patients.
Coverage for Out-of-Network Services: Beneficiaries can get reimbursement for OPD/IPD and supporting services, typically as pre/post hospitalisation expenses. These expenses may include:
Diagnostic tests
Doctor consultations, medications, rehabilitation, therapies, etc.
Medical supplies and equipments
Risk Mitigation: For patients, insurance coverage and reimbursement claims mitigate the financial risk associated with unexpected medical expenses. Policyholders feel protected knowing that a significant portion of their healthcare expenses will be covered.
Challenges of Reimbursement Claims in Healthcare
Financial burden on policyholders : As reimbursement claims require policyholders to pay for medical expenses out of pocket at non-network facilities. It may lead to financial stress or even medical debts for the patients. Policyholders often experience delays in receiving reimbursement payments, which can further exacerbate their financial condition. These delays can be due to various factors, including claim reviews and administrative processes.
Compromised healthcare outcomes : As individuals have to make upfront payments to the providers; they may avoid or delay necessary treatments.
Degraded patient experience : Policy exclusion and claim rejections may lead to dissatisfaction and trust deficit among policyholders. It will have negative effect on the health insurance sector, resulting in a decrease in participation and buying.
Administrative Burden: The process of submitting and processing reimbursement claims can be highly administrative and complex.Policyholders often need to seek help from as dedicated BSPs or third-party billing services to manage the paperwork efficiently.
Fraud and Abuse: The complexity of the reimbursement process can also create opportunities for fraud and abuse. Dishonest practices such as upcoding or unnecessary procedures can lead to overbilling, which harms both patients and payers.
Typical/existing workflow for OPD reimbursement insurance claims
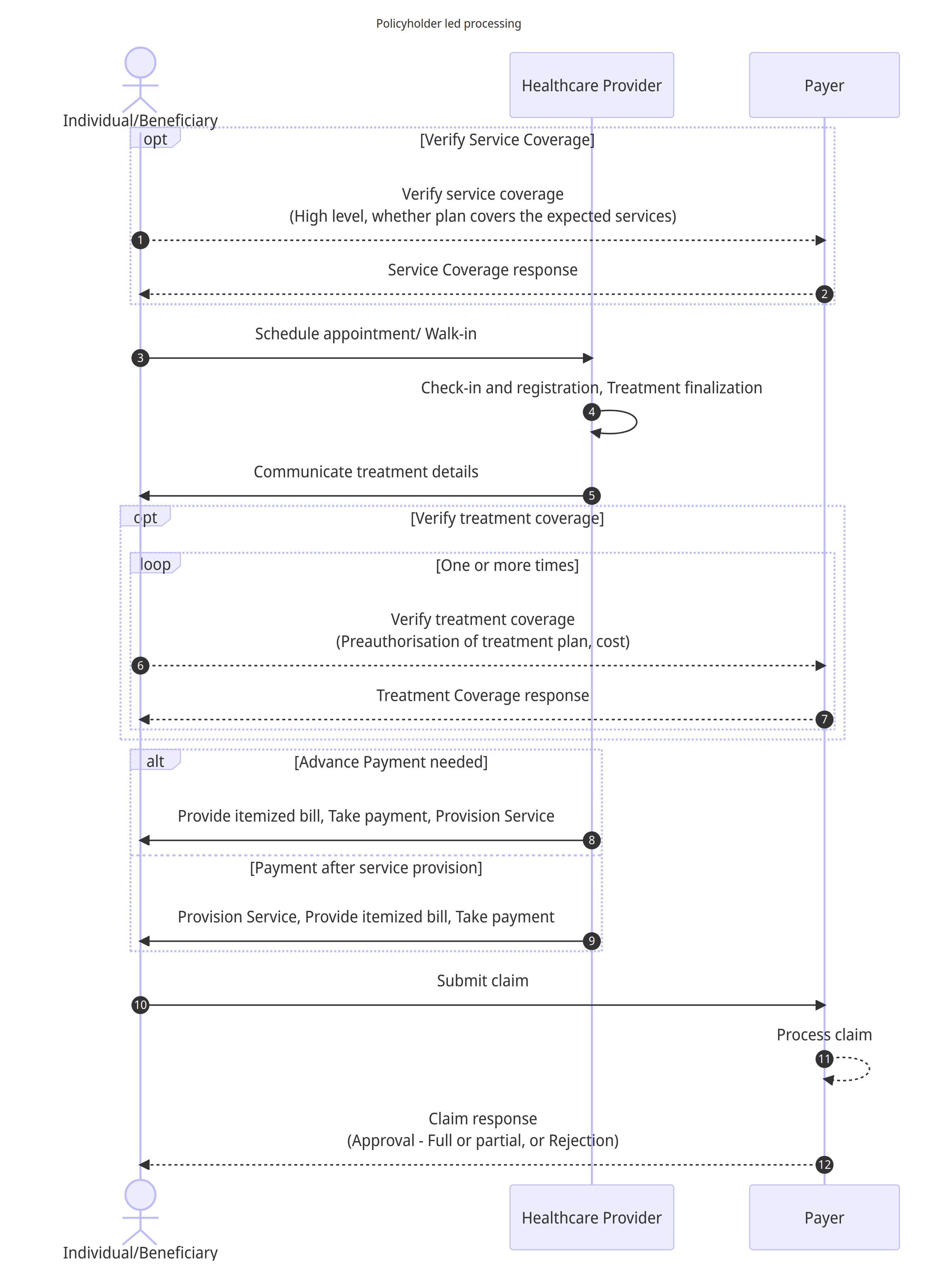
Workflow details
(Optional) The Individual initiates the process by contacting the Payer to verify service coverage, seeking high-level information about whether the insurance plan covers the expected services. The policyholder could also do this step after seeking the appointment/walk in.
(Optional) The payer responds back with eligibility details.
The Individual schedules an appointment or arrives as a walk-in at the Healthcare Provider's facility.
The Healthcare Provider proceeds with check-in, registration, and finalizing the treatment plan based on the Individual's requirements.
The Healthcare Provider communicates the treatment details to the Individual, providing necessary information about the proposed course of action for the treatment or services.
(Optional) The Individual contacts the Payer to verify treatment coverage, seeking preauthorization for the proposed treatment plan and obtaining cost details if required by the insurance policy. Wherever applicable, this step may be repeated multiple times to signal change in treatment/service plan.
(Optional) The payer responds back with the preauthorization response for each request.
In the case where an advance payment is required, the Healthcare Provider provides an itemised bill to the Individual, takes the fees and provisions of the required services, such as consultation, tests, drugs, products, therapy sessions, or any other relevant treatments.
Alternatively, if payment is to be made after service provision, the Healthcare Provider directly provides the necessary services, then presents the Individual with an itemised bill detailing the fees and receives payment.
The Individual submits the claim to the Payer, providing all relevant documents and information needed for claim processing.
The Payer processes the submitted claim, reviewing the details and documents provided by the Individual (or the Healthcare Provider).
The Payer responds to the Individual with the claim outcome, which could be approval (full or partial) of the claim or rejection, with the applicable reimbursement amount based on the policy coverage.
Following subsection provides details on mapping the OPD workflows onto the HCX protocol.
Last updated
Was this helpful?